AMD’s flagship GPUs are making a strong comeback, powered by their next-generation RDNA architecture. The RDNA successor promises significant performance upgrades, improved efficiency, and cutting-edge features aimed at competing with top-tier GPUs from Nvidia. With this innovation, AMD aims to reclaim its position in the high-performance gaming and computing market. Stay tuned for more details as AMD reshapes the GPU landscape.
A recent leak on the Chiphell forums has revealed AMD’s ambitious plans for its upcoming CPU and GPU architectures. According to a post by forum member zhangzhonghao and AMD is preparing to the utilized TSMC’s cutting-edge N3E process node for next-generation Radeon GPUs and potentially for some of the future CPUs.
Leak highlights his the development of GPUs based on the new UDNA architecture and which will succeed the current RDNA.
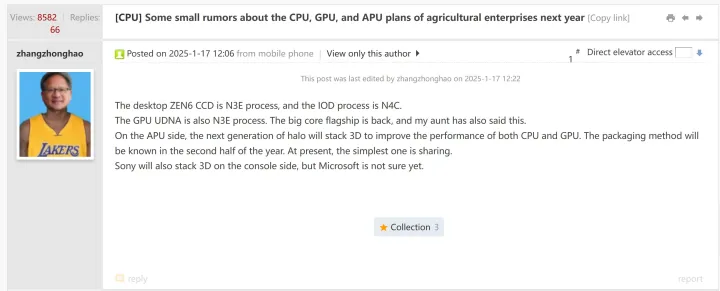
AMD confirmed that a working on UDNA at IFA last year, which expected to span across gaming and enterprises. AMD has announced their unified UDNA GPU architecture. The company previously developed separate GPU architectures, RDNA for gaming and CDNA for compute, which, while successful, created inefficiencies in its GPU hierarchy. The new UDNA architecture aims to unify these designs, simplifying development and enabling streamlined software optimization across all AMD GPUs.
The use of TSMC’s N3E node, an enhanced version of the 3nm process, indicates a focus on improving performance and efficiency. This technology expected to deliver higher transistor density better power management, which could translate into enhanced gaming and computer capabilities. The UDNA architecture may also feature upgrades for ray tracing and AI workloads, areas where AMD has lagged behind the competition.
Key Features and Innovations:
- Enhanced Performance: The RDNA successor is rumored to deliver significant boosts in performance, leveraging advanced technologies like chieaplet design and increased clock speeds. This should make AMD GPUs more competitive in gaming and productivity workloads.
- Energy Efficiency: Building on RDNA 2’s success, the new architecture will focus on better performance-per-watt metrics, ensuring powerful GPUs that consume less energy without compromising output.
- Ray Tracing Advancements: AMD is expected to make major strides in real-time ray tracing, bringing their capabilities closer to or even surpassing Nvidia’s offerings.
- AI-Powered Features: Similar to Nvidia’s DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling), AMD’s FSR (FidelityFX Super Resolution) is likely to receive substantial upgrades to improve frame rates and visual quality, with potential AI-driven enhancements.
- Support for PCIe 5.0 and Faster Memory: The RDNA successor is expected to support cutting-edge standards like PCIe 5.0 and high-speed GDDR6 or even GDDR7 memory, ensuring lightning-fast data transfer and rendering.
Market Impact:
With Nvidia’s dominance in the GPU space, AMD’s RDNA successor is poised to level the playing field.
Release Timeline:
While exact details are still under wraps, AMD is likely to reveal more about the RDNA successor during major tech events in 2025.
Why It Matters:
AMD’s RDNA successor represents a pivotal moment for the company, signaling its commitment to innovation and competition.

Leave a Reply